A scaling law beyond Zipf’s law and its relation to Heaps’ law
Published:
Font-Clos F, Boleda G and Corral A 2013 New J. Phys. 15 093033
Download PDF here
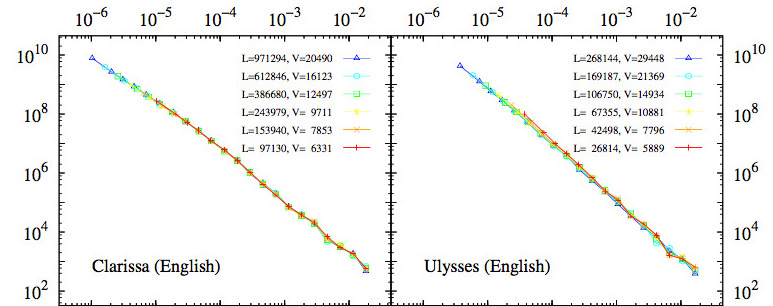
Abstract: The dependence on text length of the statistical properties of word occurrences has long been considered a severe limitation on the usefulness of quantitative linguistics. We propose a simple scaling form for the distribution of absolute word frequencies that brings to light the robustness of this distribution as text grows. In this way, the shape of the distribution is always the same, and it is only a scale parameter that increases (linearly) with text length. By analyzing very long novels we show that this behavior holds both for raw, unlemmatized texts and for lemmatized texts. In the latter case, the distribution of frequencies is well approximated by a double power law, maintaining the Zipf's exponent value γ sime 2 for large frequencies but yielding a smaller exponent in the low-frequency regime. The growth of the distribution with text length allows us to estimate the size of the vocabulary at each step and to propose a generic alternative to Heaps' law, which turns out to be intimately connected to the distribution of frequencies, thanks to its scaling behavior.
